 Hypermobility |
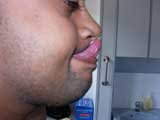 Tongue to nose(Gorlins Sign) Tongue to nose(Gorlins Sign) |
 Hypermobility |
|
Joint laxity, hypermobility, or supple (loose) joints is a widespread condition affecting 10-25% of people. The joints move beyond their normal range and hence cause recurrent minor injuries to joints and adjacent structures (muscles, ligaments, etc.). These injuries lead to chronic mild pain at various sites that does not require treatment. Hypermobile joints can be an asset for some people, such as dancers, musicians (particularly instrumentalists), gymnasts, and yoga practitioners. It is neither arthritis nor any other disease: it is a natural variation in the composition and flexibility of body tissues. Females are usually suppler than males. Features: Pain at various joints, particularly hands, hips, and knees, after an unusual activity is a common complaint of hypermobile people. Pain can disturb sleep at night and is usually relieved by morning. Sprains are frequent in the ankle and other joints. Muscles and ligaments are prone to tear, and joints can swell due to fluid. A higher grade of laxity can lead to unstable joints and recurrent dislocations. Back pain and soft tissue rheumatism can also occur. Repetitive trauma and recurrent dislocations lead to joint damage and consequent degenerative arthritis. Some of these patients are very tall and slim with long and slender fingers. Skin can be thin and stretchy with scarring from minor cut injuries. Drooping eyelids, slanting eyes, short-sightedness, varicose veins, hernia, and prolapse of rectum or uterus are some other features associated with this condition. You can find out whether you are hypermobile from the Beighton Score (5 or more out of 9 points). You can still be hypermobile if you have less than 5 points along with some of the features mentioned above. Genetic Causes: Joint hypermobility is called benign if the joints are not unstable. In rare cases, joint hypermobility can indicate a more generalized and usually inherited disease such as Marfan’s syndrome (tall stature, long slender limbs, deformed spine, and thoracic bones, problems of eyes and blood vessels, etc.), Osteogenesis imperfecta (fragile bones), and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (many subtypes). Many patients with these disorders have soft skin, easy bruising, dental crowding, high arched palate, hernias, and early osteoarthritis. Other organs such as the eye, ears, large blood vessels, and heart can also be involved. There are no confirmatory laboratory tests, and genetic testing is costly. Avoidance of high-impact joint activity and regular exercise are necessary for the management of these diseases. Treatment: The pain due to hypermobile joints can be reduced with gentle strengthening exercises and pain killers like paracetamol. More potent painkillers may be required for severe pain. Surgical stabilization of joints provides a temporary and partial improvement in most cases. |
||
